News, SPPIN seminars
16 apr. 2024 – Anna BENCSIK – Environmental Toxins and Parkinson’s Disease: What Do Mouse Models of Realistic Paraquat Exposure Reveal?

Anna BENCSIK – Université Lyon 1 ANSES
SPPIN’s webinar 2024, 16 april at 11h30 in room salle des Thèses (3e étage campus Saint-Germain)
Environmental Toxins and Parkinson’s Disease: What Do Mouse Models of Realistic Paraquat Exposure Reveal?
Parkinson’s disease, the second most common neurodegenerative disease in the world, belongs to the α-synucleinopathies’ family, which are characterized by the accumulation of a pathological form of α-synuclein (α-syn), a neuronal protein whose precise roles are still poorly defined. The etiology of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, but risk factors have been identified, such as exposure to environmental factors. Among them, pesticides have been epidemiologically linked to the early onset of Parkinson’s disease in farmers, and some substances, such as paraquat, a widely used herbicide, have become a reference substance in the studies of α-synucleinopathies. Paraquat administered to mice peripherally or intracerebrally induces parkinsonian pathology including α-syn aggregations or specific losses of dopaminergic neurons. However, in order to decipher the role of paraquat as an environmental factor in Parkinson’s disease, it is necessary to carry out studies mimicking more realistic exposures. We will present the different paraquat exposure strategies we have implemented (ingestion, inhalation or via pregnant females) in different animal models (wild or transgenic mice expressing mutated human α-syn), and what they reveal about its neurotoxic effects triggering or accelerating the pathological process of Parkinson’s disease.
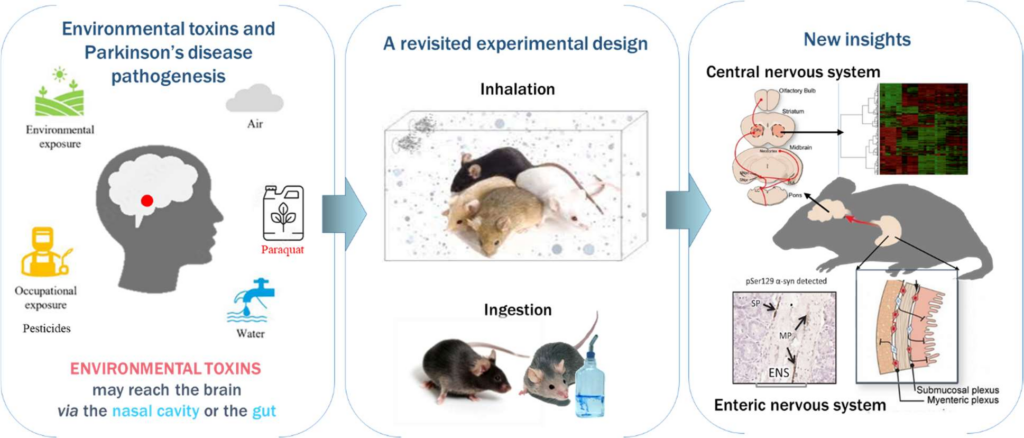
- Hamdaoui, Q., et al., Prenatal exposure to paraquat and nanoscaled TiO2 aerosols alters the gene expression of the developing brain. Chemosphere, 2022. 287(Pt 3): p. 132253.
- Naudet, N., et al., Oral Exposure to Paraquat Triggers Earlier Expression of Phosphorylated alpha-Synuclein in the Enteric Nervous System of A53T Mutant Human alpha-Synuclein Transgenic Mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol, 2017. 76(12): p. 1046-1057.
